What is a Stop order?
The stock market is a crazy place where prices fluctuate like a rollercoaster. The wonderful thing is that you have tools at your disposal to assist you in maintaining control. It is one of these instruments, and it’s like having your superhero cape for handling stock price fluctuations.
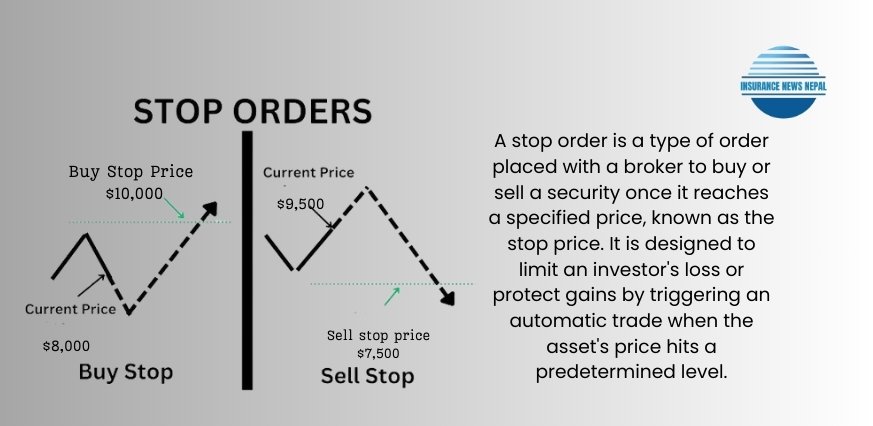
So, to put it simply, what is a stop order? Essentially, it’s a letter that you give to your broker instructing them to purchase or sell a stock at a specific price. We refer to this particular position as the “stop price.” Consider it a warning indicator, similar to a red flag, alerting your broker to a potential trade opportunity when the stock hits a price you have already determined. It’s how you keep yourself informed and safeguard your investment.
[ez-toc]
What are the types of Stop orders?
Sell stops
Consider sell stops to be safety valves for your financial investments. The system automatically sells your shares if the price of a stock drops below a certain threshold that you establish (for example, $45 for a stock that you purchased at $50). This protects your gains if the market declines and helps you minimize your losses if things go south.
Buy Stops
Consider buy stops as buttons for automatic purchases. The method will automatically purchase shares for you whenever a stock hits a preset price (let’s say $25 for a stock now trading at $20). In this manner, you can profit from a possible increase in the stock’s value without investing too soon.
Trailing Stops
Consider trailing stops as traffic-sensitive smart lights. These stops fluctuate in value in tandem with asset prices, consistently remaining a certain percentage below the going rate. You have more room for gains if the price increases because the stop price also increases.
The stop price moves with the price, shielding you from sharp declines.
How does Stop Order work?
Select Your Indicator
Select a pricing point; it’s like putting up a warning sign for the market. This point may be either above the current price (buy stop) or below it (sell stop).
Await the Signal
Visualize a dance floor in the market. Similar to waiting for a rollercoaster to reach the peak before beginning the ride, your order remains silent until the market reaches the price you have selected.
The signal is on! It’s Action Time
Whoa! When the market hits the price you’ve set, your order goes into effect and becomes a market order.
Market Order Takes Over
The market is now taking the lead. Due to fluctuations in the market, the price at which your order is filled may fluctuate somewhat from the one you have selected.
Purchase or Dispose as Scheduled
Your order will either seize the security (buy stop) or release it (sell stop) according to the signal you have selected. Imagine it like automatically getting off the rollercoaster at the precise location you select.
When do you place a stop order?
- Locking in Wins
Don’t forget to lock in your wins if you’re having them! Put a sell-stop order below the going rate. Your shares automatically sell if the market declines past that amount, protecting your earnings.
- Reducing Losses
If your stock isn’t doing well, set a cap on how much you can lose. Put a sell stop below the purchase price. Your order takes effect and lessens your losses if the stock continues to decline.
- Seizing Chances
Do you believe a stock is going to rise? Place a purchase-stop order above the going rate. Your order is automatically placed if the stock rises beyond that threshold, allowing you to profit from the upward trend.
- Playing it Safe When Wagering Against
Exercise caution when wagering on a stock’s decline. Above the price of your short entry, place a purchase stop. Your order limits the amount you could lose if the stock rises suddenly.
- Avoiding Market Jitters
Exercise caution when the market is erratic. When making new investments during volatile times, use stop orders. By doing this, you can stay out of the unexpected declines and increases in the market.
What are the examples of Stop orders?
Avoiding Big Losses
Sarah paid $50 for each of the 100 shares of ABC Company that she now owns. She puts in an order to sell them automatically if the price goes to $40 or less to make sure she doesn’t lose too much money. That way, if things don’t work out, she will have less money to lose.
Seizing Chances
David is monitoring XYZ stock, which is trading at $20. Though he is cautious about making an early purchase, he believes it may rise. Therefore, he places a buy order that will be automatically filled if the stock price rises to $25 or higher. In this manner, he can ride the wave and possibly profit if the stock continues to rise.
Playing it Safe When Betting Against a Stock
Maya is “shorting” the DEF stock, which is speculating that it will decline. She places an order to automatically purchase the stock if its price hits $45 or higher to safeguard herself if the stock unexpectedly rises. If things don’t work out as planned, this helps her reduce the amount of money she could lose.
You may also like:
FAQs
What needs to happen to stop disequilibrium from occurring?
What is a buy-stop order?
What is a stop-limit order to sell?
How does a stop-limit order work?
What is a stop market order?
Conclusion
To successfully navigate the ever-changing financial markets, stop orders are an indispensable instrument. These tools enable investors to manage their portfolios proactively, whether it’s by using buy-stop orders to capture possible breakouts, stop-limit orders to make smart sell decisions, or stop market orders to react quickly to market fluctuations. People may improve their risk management, safeguard earnings, and take advantage of market chances by learning how to use stop orders wisely. This will ultimately help them adopt a more robust and controlled attitude to their investing journey.